Climate of Japan
Outline of climate of Japan
There is extensive continent to the west of Japan.
There is Sea of Japan between the continent and Japan.
And there is vast Pacific Ocean to the east and south.
Warm ocean currents flow northeastwardly off the coast of Japan.
This situation moves the various air masses around Japan, so unique four seasons in Japan are created.

Climate classification of Japan
The land of Japan mainly belongs to the temperate zone.
But, the area of Japan is wide.
The north part such as Hokkaido belongs to the subarctic zone and the climate is similar to northern Europe.
The south part such as Okinawa Islands belongs to subtropics and the climate is similar to Taiwan, Hawaii, the Philippines, etc.
Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu islands are in the temperate zone.
But, there are relatively high mountains along the long lands.
So, the climates in the sides of Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan differ.
Especially, in winter, much snow falls in the areas facing the Sea of Japan.
Japanese people are sensitive to weather changes.
In daily conversation, they often talk about the topics about the weather.
Spring (March to May)

Canola flowers and cherry blossoms in a rural area
During winter, the air mass from very cold Continent covers Japan.
From around late February, it becomes weak little by little.
In March, the sunshine becomes a little warm.
Because the air mass of cold Continent becomes weak, low pressures often pass around Japan from west to east.
When a low pressure passes, rain falls.
After rain, the temperature falls a little, but it is getting warmer and warmer.
This is the climate of spring in Japan.
From around the end of March, "sakura" (cherry blossoms) begins to bloom in the south part of mainland.
This is the start of mid-spring.
It becomes in full blooming in the early April, and the scene gradually moves northward.
All Japanese people realize the coming of spring by "sakura".
From around late April to May, the temperature continue to rise little by little.
In this season, we feel very comfortable.
Many days are nice weather, and the season move to early summer.
Tsuyu (Mid-June to mid-July)

Hydrangeas in Meigetsuin temple in Tsuyu season
Hot and wet air mass on the Pacific Ocean to the south of Japan becomes stronger gradually in June.
Dry air mass of the continent and the air mass on the ocean start struggling with each other, and a stationary front is formed around Japan from west to east.
Around the stationary front, rainy or cloudy weather continues every day.
The temperature approaches 30°C and the air is humid.
In Japan, this rainy season is called as "tsuyu" or "baiu", and the stationary front is also called "baiu front".
Tsuyu lasts for about a month.
In mid-July, the hot and wet air mass increases its strength and pushes the the stationary front up to the north gradually.
In the southern areas of the stationary front, rain clouds disappear.
And strong sunshine and hot air cover the area.
On the day, Japan Meteorological Agency announces the end of tsuyu ("Tsuyu-ake" in Japanese) in the area.
It is also the start of mid-summer.
Summer (Mid-July to mid-September)

Shirakawa-go in mid-summer
Wide area of Japan is covered with hot high pressure on the Pacific Ocean.
It sends hot and moist air to Japan.
In many areas, the temperature is over 30°C, and the humid is high.
Recently, the temperature reaches between 35°C and 40°C in many cities.
When you travel around Japan in this season, you must be careful of heat stroke.
In addition, the temperature is over 25°C even in the night.
Such night is called as "tropical night" in Japanese.
We cannot sleep well on the nights.
Sometimes, towering thundercloud appears locally in the day, and there is a sudden shower.
It often causes the thunderbolt and sudden flood.
In addition, typhoons are often born on the Pacific Ocean, and a few of them come to Japan in this season every year.
Like hurricane and cyclone, it causes violent storm in the wide areas while moving.
At that time, railways, airplanes, buses are stopped in advance.
That will affect your travel around Japan.
The climate of Japan may be suffering from the effects of global warming.
It is obvious that summer in Japan is getting hotter and longer.
Autumn (Mid-September to early December)

Autumn leaves in Eikando temple in Kyoto
In the mid-September, the air mass of the Continent is becoming strong again and it sometimes sends dry and cool air to Japan.
The air mass of the ocean begins to withdraw, because the lengths of day and night will be nearly equal and the power of the sun is weakning.
Both air masses struggle with each other again, but the period is not so long as tsuyu.
In mid-October, cool and comfortable season comes in the mainland again.
The climate in October and November is like April and May.
Rather the air is drier than the season of spring.
In autumn, low pressures sometimes pass on Japan from west to east.
Cold rain falls at that time, but it is generally fine on the other days.
The days are getting shorter and shadows become longer.
And, the leaves begin to color from the northern areas.
Winter (Mid-December to February)

Higashi-Chaya District in Kanazawa city in winter
In November, Siberia in the eastern part of Russia is getting very cold and the dominant high-pressure is formed.
From the cold high-pressure, very cold air flows toward Japan.
The temperature in Japan is falling gradually.
On the other hand, the low-pressure is formed on the ocean to the east of Japan in opposition to very strong Siberia high-pressure.
Therefore, the cold air is accelerated and it blows toward Japan as a strong northwesterly wind.
The wind is very dry in the continent, but it crosses the Sea of Japan which is relatively warm.
The wind absorbs much water-vapor from the sea and reaches the islands of Japan.
Steep mountains stand up on the islands, so the wet wind scrambles up the mountains and makes thick clouds extensively.
Because the clouds contain considerable moisture and the temperature is low, much snow fall there.
Therefore, the areas along the Sea of Japan have many snowy days in winter.
The northern part of the area is one of the world's heaviest snowfall areas.
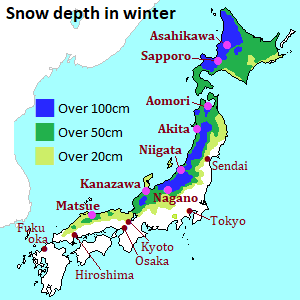
Snow covers most cities, towns, villages and mountains during the winter.
There are a lot of ski resorts in the area.
The cold wind which has lost moisture crosses over the mountains.
And the dry wind blows down to the areas of the Pacific side.
The area along the Pacific Ocean has many big cities such as Tokyo, Nagoya, Kyoto, Osaka, etc.
Fine weather continues almost every day in these areas.
It snows only a few times a year in these areas.
Climate in Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu Islands

Cherry blossoms in Tokyo
Honshu, Shikoku, Kyoshu islands are the main part of Japan.
As mentioned above, these areas have the four seasons and rainy tsuyu season.
Honshu Island has an arc shape.
The northeast part is long from north to south, and there is Tohoku Region.
The other part is long from east to west, and the east end is Kanto Region including Tokyo.
Because the area is almost on the same the latitude, the climate is also similar.
In the area, spring starts from March, tsuyu (rainy season) continues from mid-June to mid-July.
Midsummer in the mainland of Japan is very hot and humid.
Recently, the temperature in many cities often exceeds 35°C.
Autumn comes around mid-September, and real winter starts in the late December.
In the south side of the area, it is fine and dry in most days in winter.
But the north side of the area facing the Sea of Japan has much snow in winter.
Tohoku Region is a little cooler than the area.
Spring comes 2 to 4 weeks later than Tokyo, and winter comes 2 to 4 weeks earlier than Tokyo.
The climate in Shikoku and Kyushu are also similar to Honshu.
But Shikoku and the south part of Kyushu are warmer than the other areas.
Climate in Hokkaido Island

Sapporo Snow Festival in February
Hokkaido is the northernmost region in Japan, so the climate is cooler than the other regions.
Winter starts from late November and ends in late April.
It snows in the whole area, but the southeastern area near coast has less snow than the other area.
In January and February, the temperature in most areas in Hokkaido becomes below the freezing point.
Especially, the temperature in the inland area falls down to 10°C below zero, and sometimes 20 to 30°C below zero.
On the other hand, the temperature in midsummer is unexpectedly high and becomes over 30°C sometimes.
But because the humidity is lower than Honshu, the climate is comfortable.
Climate in Okinawa Islands

A beach in Okinawa
The islands in Okinawa area belong to the subtropical regions.
Of course, the climate is warm and the area has no cold season.
Snow fell in Okinawa only twice in about 60 years.
Even in midwinter, the temperature in a day is over 15°C.
In summer, the temperature in a day is 30 to 33°C.
But it is lower than the temperature in the mainland of Japan because the small islands are surrounded by wide ocean.
And squalls occured often in summer.
Typhoon
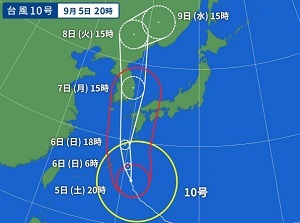
A predicted course of a typhoon in a weather report (Typhoon No.10 on Sep.5, 2020)
There is the vast Pacific Ocean to the south of Japan.
Near the equator of Western Pacific Ocean, more than twenty typhoons develope every year.
"Typhoon" is a strong tropical cyclone in Western Pacific Ocean, and it is the same as "hurricane" in eastern Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean and "cyclone" in South Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean.
The central atmospheric pressure is extremely low, and very strong wind blows toward the center like a huge whirlpool.
Therefore, fierce storm causes within several hundred kilometers.
In general, a typhoon moves toward the northwest or the west, then it turns toward the northeast or the north at around a latitude of 20 degrees north by westerlies.
The moving speed is 10 to 40 km/h.
Every year, 2 to 6 typhoons hit Japan from the southward and pass through the mainland of Japan toward the northeast or north.
Most of them come to Japan between July and October.
Especially, the typhoons hitting Japan peaks in August and September.
In a place where a typhoon passes, the storm rages for some hours to half day.
Landslide disaster, wind damage and flood often occurs.
After a typhoon is born in the ocean, it reaches Japan in 3 to 7 days.
The weather forecasts on TV and radio say early about detailed information of the typhoon which has a possibility to come to Japan.
Pay attention to the weather forecast when you visit Japan in this season.
If a typhoon is coming, it causes traffic confusion in the wide areas in Japan.
Recently, it is announced in advance that the operations of railways, airplanes, buses are suspended during the typhoon.
You will be forced to change your travel schedule.
By the way, each typhoon has a name of person in most countries, but the ordinal number in the year is given to the typhoon in Japan.

